Get your EPOC on
Basics:
This is a concept that came to my attn when I was in my undergrad. Just to discover that I could put a fancy name to the style of workouts that I was already engaging in, especially as a collegiate level hockey player.
Basically, utilizing the basic principles behind EPOC, you can make your workouts more efficient and effective.
- High Intensity
- Short Duration
- Constantly varied in tempo and type of workout.
Why is it effective?
Looking at the Research will give you the best understanding, and once I get time to actually dive into it... but here's a little overview:
- Your body has to mobilize nutrients and energy to recover
- O2 has to be replenished in tissues
- Creatine phosphate systems have to be restored
- Hormonal balance
- Ventilation recovery
- Lactate breakdown
- Regulation of body Temp
- Essentially... your body needs to re-instate a resting state. Maintaining homeostasis is a high energy consuming process. This period of 'Excess post-exercise Oxygen Consumption' can las as long as 30+ hours!! aka your body will be consuming more oxygen, and utilizing more energy over this period that what you would normally consume. Aerobic training does not have this affect on the body.
We actually EXHALE our FAT... well... kinda.
Fat turns into carbon dioxide and water
Where fat goes when you lose weight
Compared to Aerobic Training
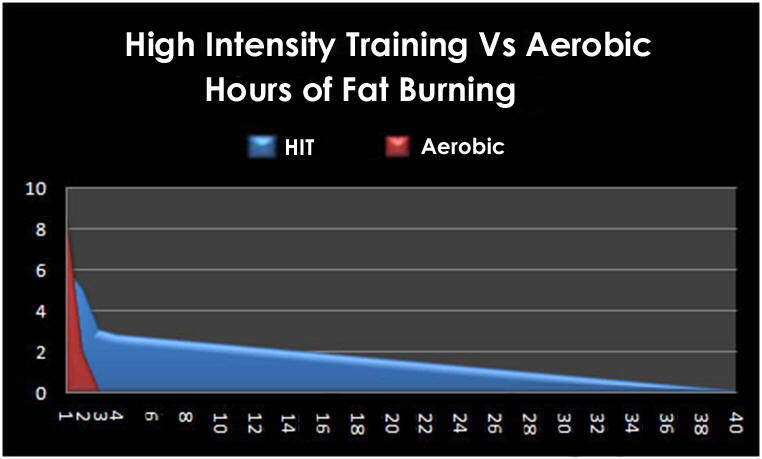


Basically the same pic..
§Changes occur rapidly
–11% in plasma
volume,
7% VO2 max, and 10% in
stroke volume with six days of training
Studies:
Sports Med. 2003;33(14):1037-60.
Effect of exercise intensity, duration and mode on post-exercise oxygen consumption.
J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Jan 1;118(1):80-5. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00697.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 13.
Transient energy deficit induced by exercise increases 24-h fat oxidation in young trained men.
Exercise Increases 24-h Fat Oxidation Only When It Is Performed Before Breakfast.
EBioMedicine. 2015 Oct 30;2(12):2003-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.10.029. eCollection 2015.
Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2006 Oct;31(5):502-11.
Acute effects of exercise timing and breakfast meal glycemic index on exercise-induced fat oxidation.
Int J Gen Med. 2015 Aug 13;8:255-60. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S87429. eCollection 2015.
Acute metabolic response to fasted and postprandial exercise.
EFFECTS OF EXERCISE INTENSITY ON EXCESS POST-EXERCISE OXYGEN CONSUMPTION AND SUBSTRATE USE AFTER RESISTANCE EXERCISE
Good Hx
Metabolic Bases of EPOC : A Review
Transient energy deficit induced by exercise increases 24-h fat oxidation in young trained men
- Fat oxidation during exercise is suppressed if carbohydrate is ingested before exercise (3, 7, 8, 9, 18, 27, 38), and the suppressive effect of carbohydrate ingestion on fat oxidation persists at least for 4 h after a meal (27). Consistent with the literature, fat oxidation during exercise was higher when exercise was performed in the postabsorptive state (AM) compared with that during exercise performed after lunch (PM)
- http://jap.physiology.org/content/118/1/80.long
From the NSCA
https://www.nsca.com/Education/Articles/Hot-Topic-Role-of-EPOC-in-Weight-Loss/
Volume Vs. Intensity


Comments